process.env.MY_ENV_VAR.
We deploy your tasks and scale them up and down when they are triggered. So any environment variables you use in your tasks need to accessible to us so your code will run successfully.
In the dashboard
Setting environment variables
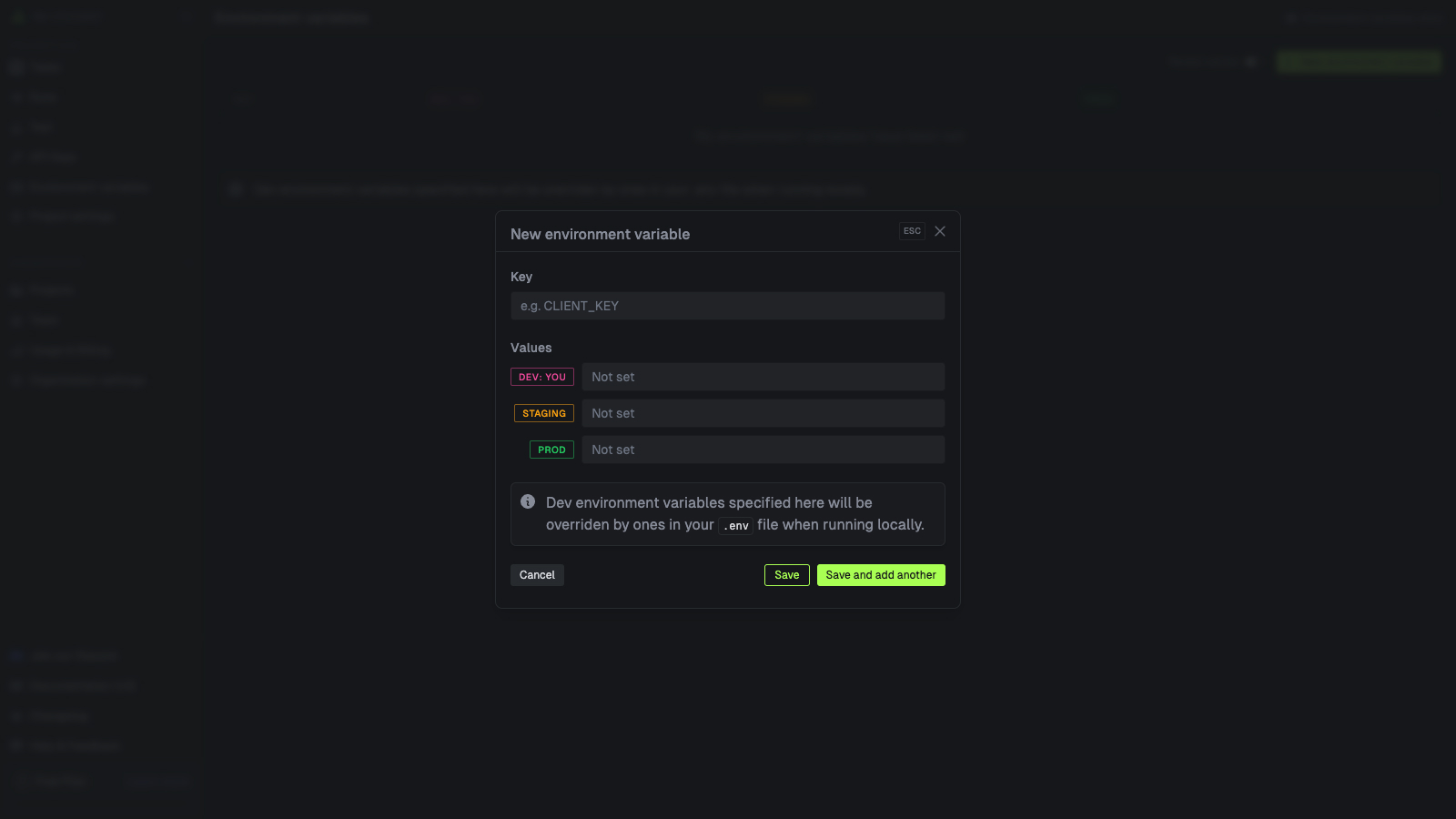
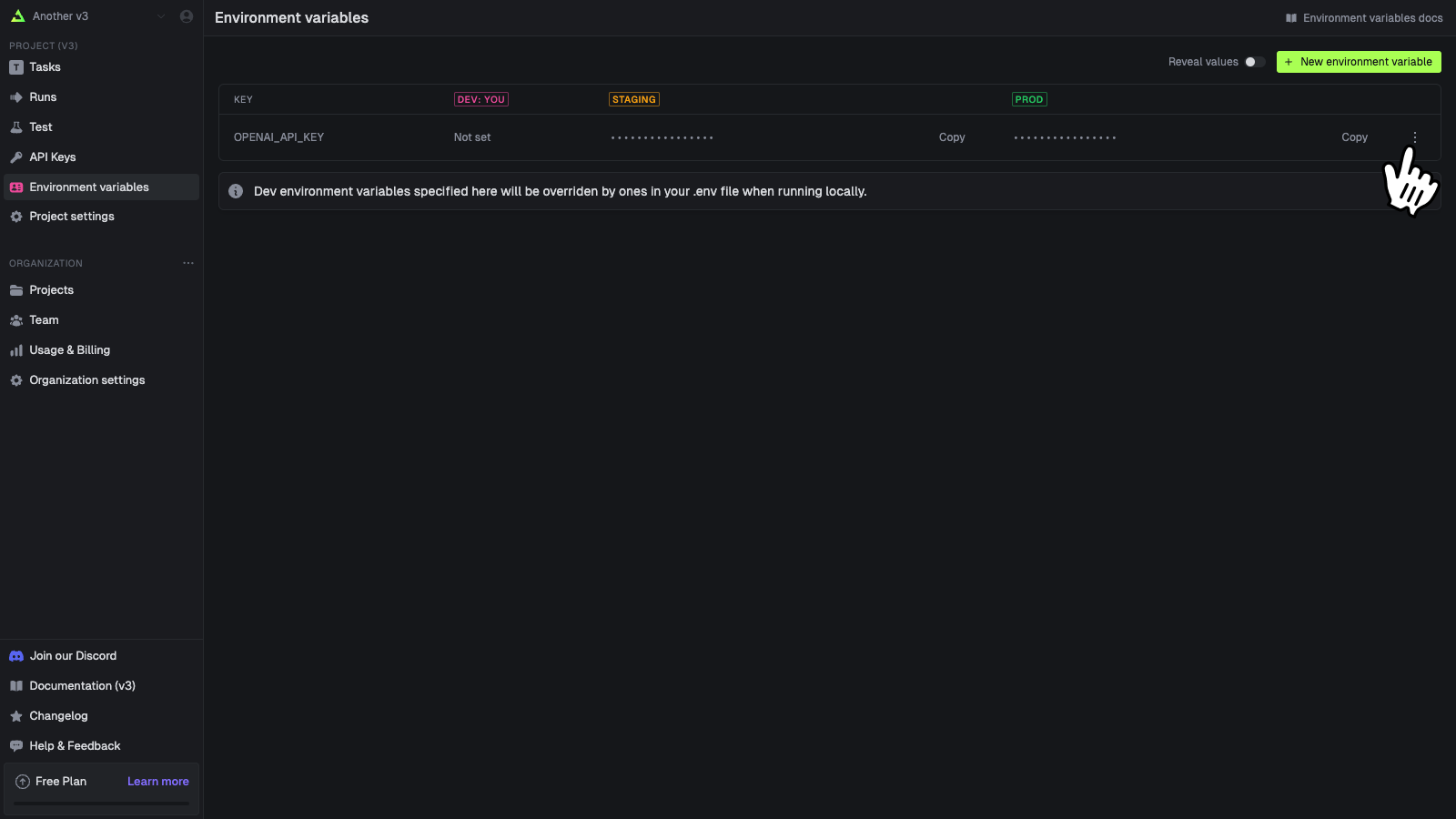
Go to the Environment Variables page
In the sidebar select the “Environment Variables” page, then press the “New environment variable”
button. 

Specifying Dev values is optional. They will be overriden by values in your .env file when running
locally.
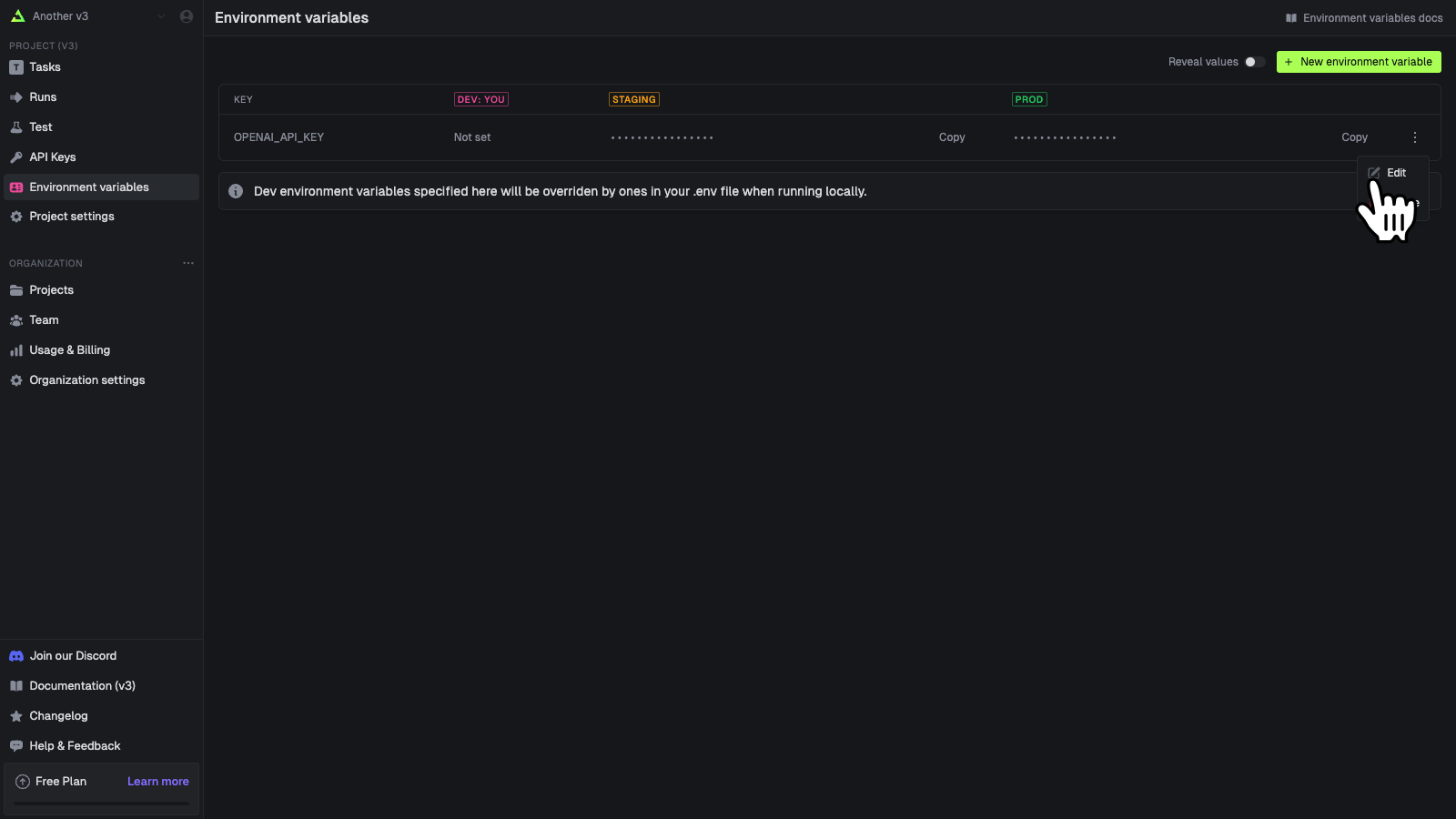
Editing environment variables
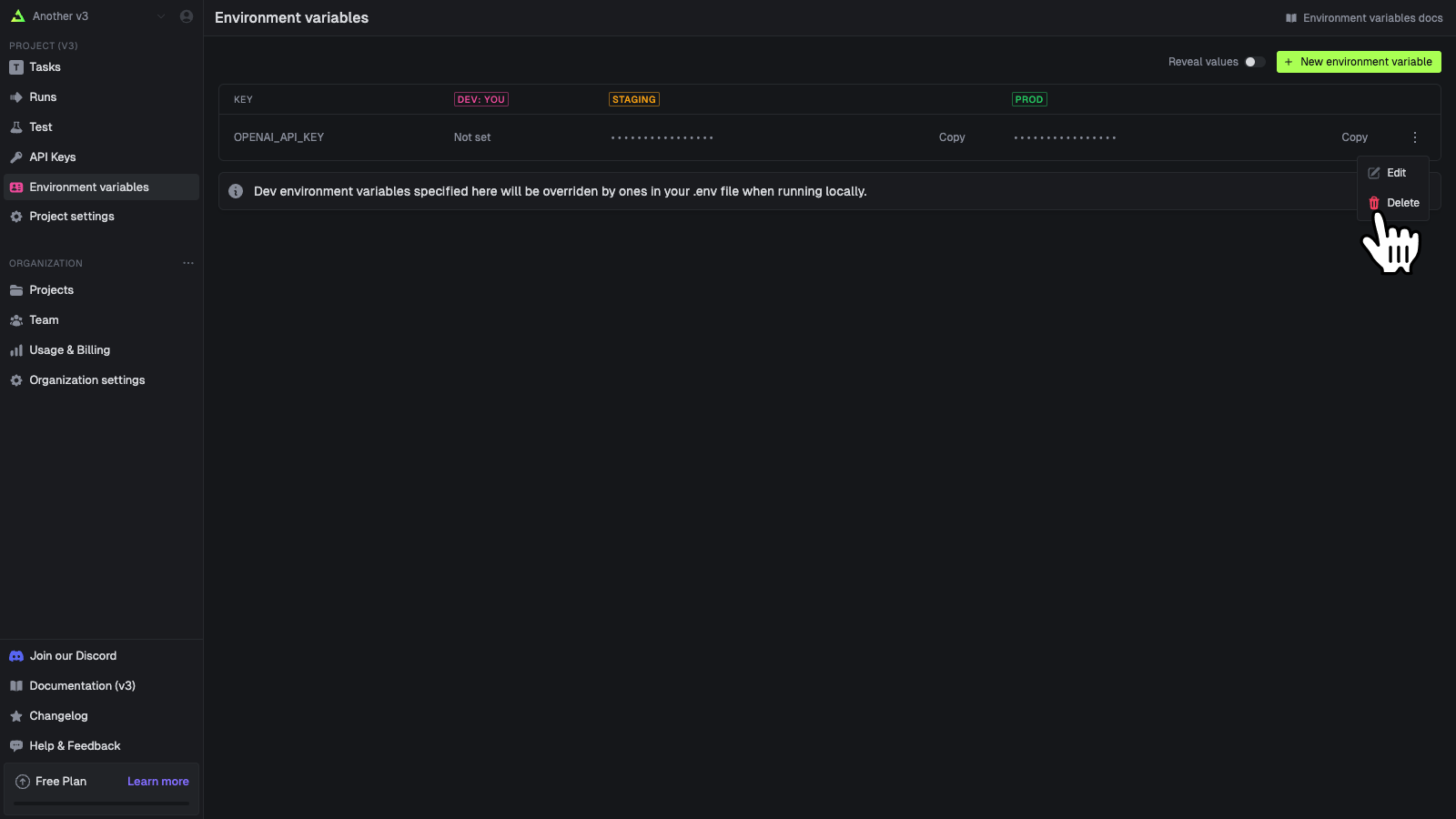
You can edit an environment variable’s values. You cannot edit the key name, you must delete and create a new one.Deleting environment variables
In your code
You can use our SDK to get and manipulate environment variables. You can also easily sync environment variables from another service into Trigger.dev.Directly manipulating environment variables
We have a complete set of SDK functions (and REST API) you can use to directly manipulate environment variables.| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| envvars.list() | List all environment variables |
| envvars.upload() | Upload multiple env vars. You can override existing values. |
| envvars.create() | Create a new environment variable |
| envvars.retrieve() | Retrieve an environment variable |
| envvars.update() | Update a single environment variable |
| envvars.del() | Delete a single environment variable |
Sync env vars from another service
You could use the SDK functions above but it’s much easier to use oursyncEnvVars build extension in your trigger.config file.
To use the
syncEnvVars build extension, you should first install the @trigger.dev/build
package into your devDependencies.trigger.config.ts
Syncing environment variables from Vercel
To sync environment variables from your Vercel projects to Trigger.dev, you can use our build extension. Check out our syncing environment variables from Vercel guide.Deploy
When you run the CLI deploy command directly or using GitHub Actions it will sync the environment variables from Infisical to Trigger.dev. This means they’ll appear on the Environment Variables page so you can confirm that it’s worked. This means that you need to redeploy your Trigger.dev tasks if you change the environment variables in Infisical.The
process.env.INFISICAL_CLIENT_ID, process.env.INFISICAL_CLIENT_SECRET and
process.env.INFISICAL_PROJECT_ID will need to be supplied to the deploy CLI command. You can
do this via the --env-file .env flag or by setting them as environment variables in your
terminal.Dev
syncEnvVars does not have any effect when running the dev command locally. If you want to inject environment variables from another service into your local environment you can do so via a .env file or just supplying them as environment variables in your terminal. Most services will have a CLI tool that allows you to run a command with environment variables set:
The syncEnvVars callback return type
You can return env vars as an object with string keys and values, or an array of names + values.Using Google credential JSON files
Securely pass a Google credential JSON file to your Trigger.dev task using environment variables.Convert the Google credential file to base64
In your terminal, run the following command and copy the resulting base64 string:
Set up the environment variable in Trigger.dev
Follow these steps to set a new environment variable using the base64 string as the value.